The derivative of ex is ex The derivative of ex is found by applying the chain rule of derivatives and the knowledge that the derivative of e x is always e x, which can be found using a more complicated proof differentiate wrt x x^y=e^(xy) Share with your friends Share 0 let u = x y and v= e (xy) when u=x y applying log on both sides,log u= y log xdiff both sides1/u du/dx = y1/x logxdy/dxdu/dx= x y ( y/x logx dy/dx) =yx y1 x y log x dy/dxnow, when v=e (xy) diff wrt x,dv/dx = e (xy) (1 dy/dx)dv/dx = e (xy) e (xy)dy/dxfromAnswer to Differentiate y = e^x square root x By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You can

Solution Differentiate Y E X Cos X 2
Y = e^x second derivative
Y = e^x second derivative- The number e is defined by e = ∞ ∑ n = 0 1 n!Answer to Differentiate y= e^x / x^4 By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You can also ask




Solved Differentiate Y E 2 X With Respect To X Self Study 365
Derivative is the important tool in calculus to find an infinitesimal rate of change of a function with respect to its one of the independent variable The process of calculating a derivative is called differentiation Follow the rules mentioned in the above derivative calculator and understand the concept for deriving the given function toNote that the function defined by y = x x is neither a power function of the form x k nor an exponential function of the form b x and the formulas of Differentiation of these functions cannot be used We need to find another method to find the first derivative of the above function If y = x x and x > 0 then ln y = ln (x x) Use properties of logarithmic functions to expand the right side ofPopular Problems Calculus Find the Derivative d/dx y=e^ (x/2) y = e−x 2 y = e x 2 Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dx f (g(x)) d d x f ( g ( x)) is f '(g(x))g'(x) f ′ ( g ( x)) g ′ ( x) where f (x) = ex f ( x) = e x and g(x) = −x 2 g ( x) = x 2 Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set u u
E^x times 1 f' (x)= e^ x this proves that the derivative (general slope formula) of f (x)= e^x is e^x, which is the function itself In other words, for every point on the graph of f (x)=e^x, the slope of the tangent is equal to the yvalue of tangent point So if y=But historically I think that the definition of the exp function is ex = lim n → ∞(1 x n)n and the properties of this function comes from this definition as shown in this article Share edited Mar 23 '15 atTo apply the Chain Rule, set u u as tan ( x) tan ( x) Differentiate using the Exponential Rule which states that d d u a u d d u a u is a u ln ( a) a u ln ( a) where a a = e e Replace all occurrences of u u with tan ( x) tan ( x) The derivative of tan(x) tan ( x) with respect to x x is sec2(x) sec 2 ( x)
Differentiate the following function with respect to x (1 x 2) cos x Medium View solution View solution If y = e x cos x, then prove that d x d yWell that depends e^x^x is ambiguous it could mean a) math e^{x^x} /math;Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functions




If Ex Ey Ex Y Prove That Dy Dx Ex Ey 1 Ey Ex 1 Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Ex 5 7 16 Ex 5 7
The expression for the derivative is the same as the one for the original function That is The derivative of e x is e x The derivative of e x is e x This is one of the properties that makes the exponential function really important Now you can forget for a while the series expression for the exponential We only needed it here to prove the Homework Statement What is the derivative of e^y?Let's take the derivative of what well let's prove what the derivative of e to the X is and and I think that this is one of the most amazing things depending on how you view it about either calculus or math or the universe so we want to figure out but we're essentially going to prove we've I've already told you before that the derivative of e to the X is equal to e to the X which is amazing
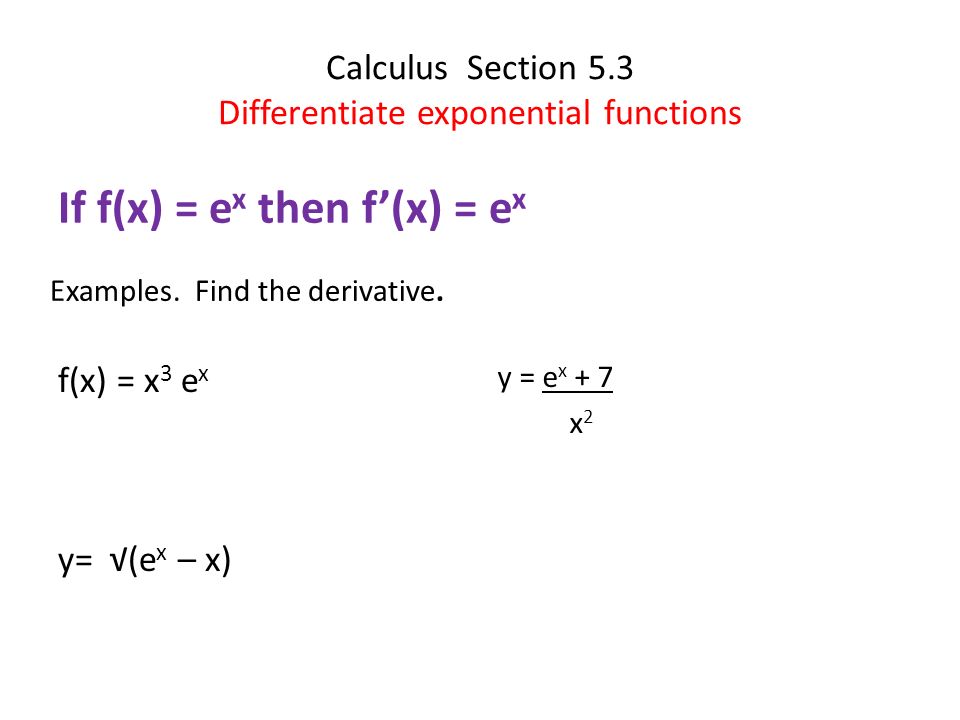



Calculus Section 5 3 Differentiate Exponential Functions If F X E X Then F X E X F X X 3 E X Y E X X Examples Find The Derivative Y Ppt Download
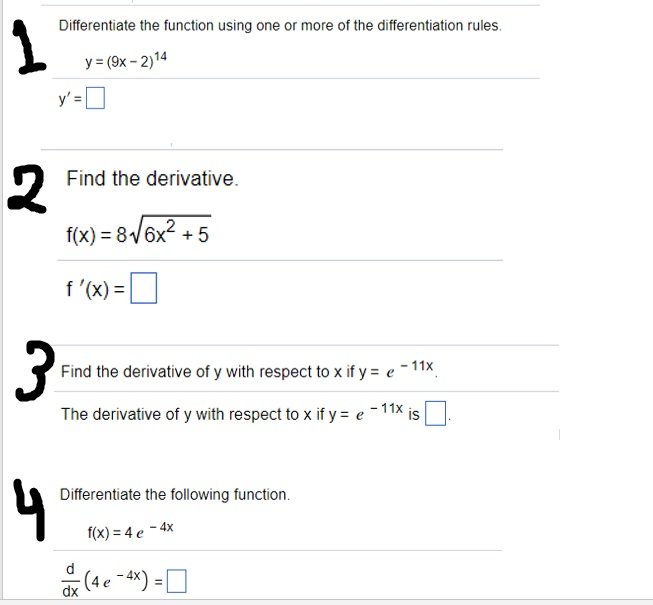



Differentiate The Function Using One Or More Of The Chegg Com
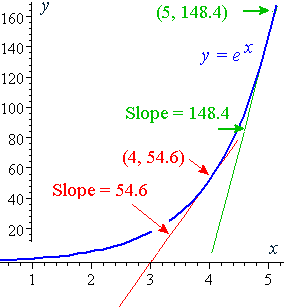
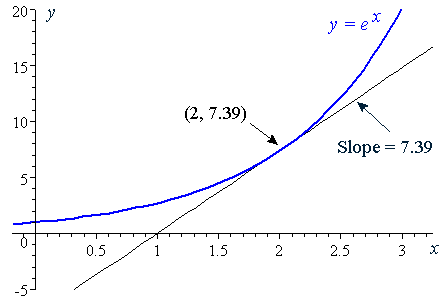
At this point, the y value is e 2 ≈ 739 Since the derivative of e x is e x, then the slope of the tangent line at x = 2 is also e 2 ≈ 739 We can see that it is true on the graph 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 x y (2, 739) slope = 739 y = e x \displaystyle {y}= {e}^ {x} y = ex ADVERTISEMENT That is, the derivative of the function ƒ (x) = e2x is ƒ' (x) = 2 e2x This derivative tells us the rate of change the output of the original function per change in input Basically, the two equations tell us that the output of the function ƒ (x) = e2x grows by a factor of 2 e2x per input So if our x value is one, pluggingY= x^ (e^x) To differentiate, first we will apply the natural logarithm to both sides ==> lny = ln x^ (e^x) We know that ln a^b = b*ln a ==> lny = (e^x) * ln x Now we will differentiate both
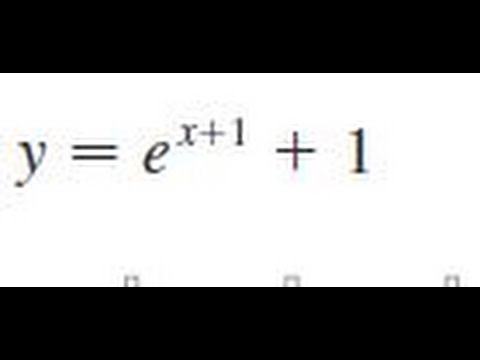



Differentiate The Function Y E X 1 1 Youtube




Differentiate W R T To Y Differentiation If Y Ex Sin X Cos X Prove That 2 Dx Dx Maths Differential Equations Meritnation Com
Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that d d x x n d d x x n is n x n − 1 n x n 1 where n = 1 n = 1 Since − 4 4 is constant with respect to x x, the derivative of − 4 4 with respect to x x is 0 0 Simplify the expression Tap for more steps Add 1Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!If the function were to be differentiable, then necessarily the left and right limits exist and agree, so we can check that The lefthand limit is the derivative of e − x at 0 and the right hand limit is the derivative of e x at 0 At zero the former is − 1 and the later is 1 so the limit doesn't exist, and the function isn't differentiable




The Derivative Of E X And Lnx



How Do You Find The Derivative Of E X Log X Socratic
X^y =e^xy The basic trick here is to remove the variable from the exponent In this case,we can take help of "ln" opereation or,lnx^y=lne^xy Taking ln on both sides or,ylnx=xylne logx^n=nlogx(1) Now,this equation can easily be differentiated or,yd/dx(lnx)lnxd/dx(y) =d/dx(xy) Here lne=1 and d/dx(uv)=ud/dx(v)vd/dx(u)Derivative of a Constant lf c is any real number and if f(x) = c for all x, then f ' (x) = 0 for all x That is, the derivative of a constant function is the zero function It is easy to see this geometrically Referring to Figure 1, we see that the graph of the constant function f(x) = c is a horizontal lineMore You will have to use the chain rule First differentiate the whole function with respect to e^x, then multiply it with the differentiation of e^x with respect to x You'll solve it Basically every composite function can be differentiated using the chain rule



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function



I Finished The Differentiation Now I Just Want The Chegg Com
(dy)/(dx)=(e^x(e^y1))/(e^y(1e^x)) Differentiating e^xe^y=e^(xy) e^xe^y(dy)/(dx)=e^(xy)(1(dy)/(dx)) or e^xe^y(dy)/(dx)=e^(xy)e^(xy)(dy)/(dx) or e^y(dy)/(dx)e^(xy)(dy)/(dx)=e^(xy)e^x or (e^ye^(xy))(dy)/(dx)=(e^(xy)e^x) or (dy)/(dx)=(e^(xy)e^x)/(e^ye^(xy))=(e^x(e^y1))/(e^y(1e^x))Method 1 math\displaystyle y = {e^{{e^x}}}/math Taking logarithm ( ln) on both sides, we get math\displaystyle \ln y = {e^x}\ln e/math Differentiating withAnswer to Let f(x, y) = e^{x^2y} sin(x y) Find the second derivative \\partial^2f/\\partial x \\partial y By signing up, you'll get thousands




If Y E X 2log X Then Dy Dx
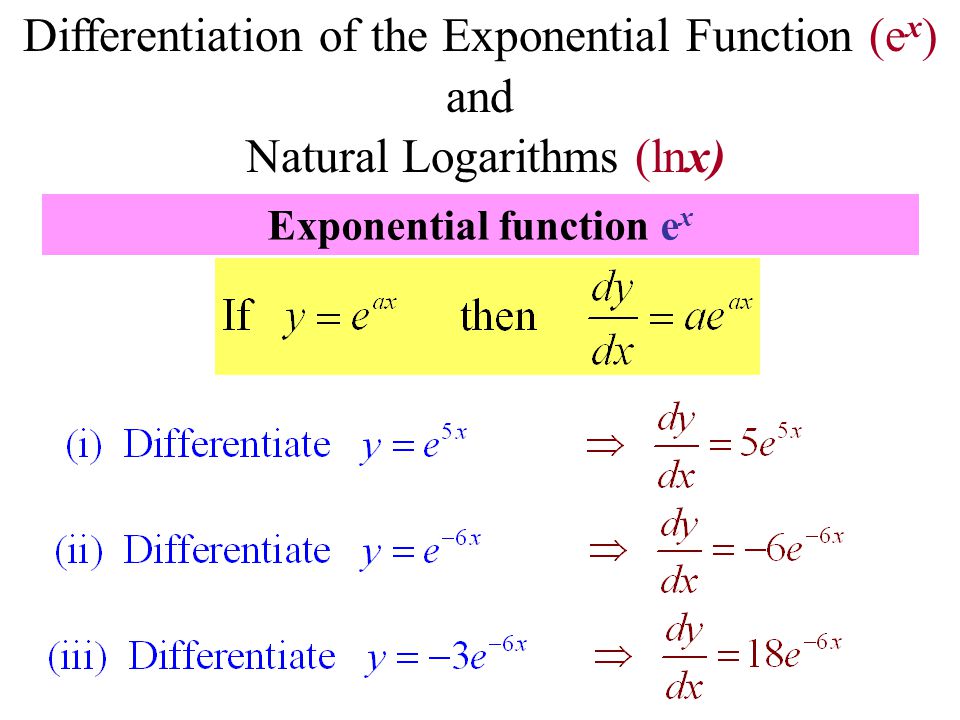



Differentiation Of The Exponential Function E X And Natural Logarithms Lnx Exponential Function E X Ppt Download
B) math (e^x)^x /math I'll do both a) You just multiply the derivative of the exponent times the exponential The exponent is math x^x=e^{x\ln x} /math, soVerify that each point lies on the graph of the unit circle (0,1) Trigonometry (MindTap Course List) The distance from (1, 2, 1) to the plane 6x 5y 8z = 34 is Study Guide for Stewart's Multivariable Calculus, 8th The directrix of the conic given by r=6210sin is a) x=53 b) x=35 c) y=53 d) y=35Differentiation y=a^x To find the derivative of y=a^x, we use the exact same steps as that used for differentiating y=e^x, and y=x^x as well Hence, if you did those earlier you should be able to do this one Just as before, you take the log on both sides This brings the x down from the power position, as shown on the RHS




Calculus Section 5 3 Differentiate Exponential Functions If F X E X Then F X E X F X X 3 E X Y E X X Examples Find The Derivative Y Ppt Download
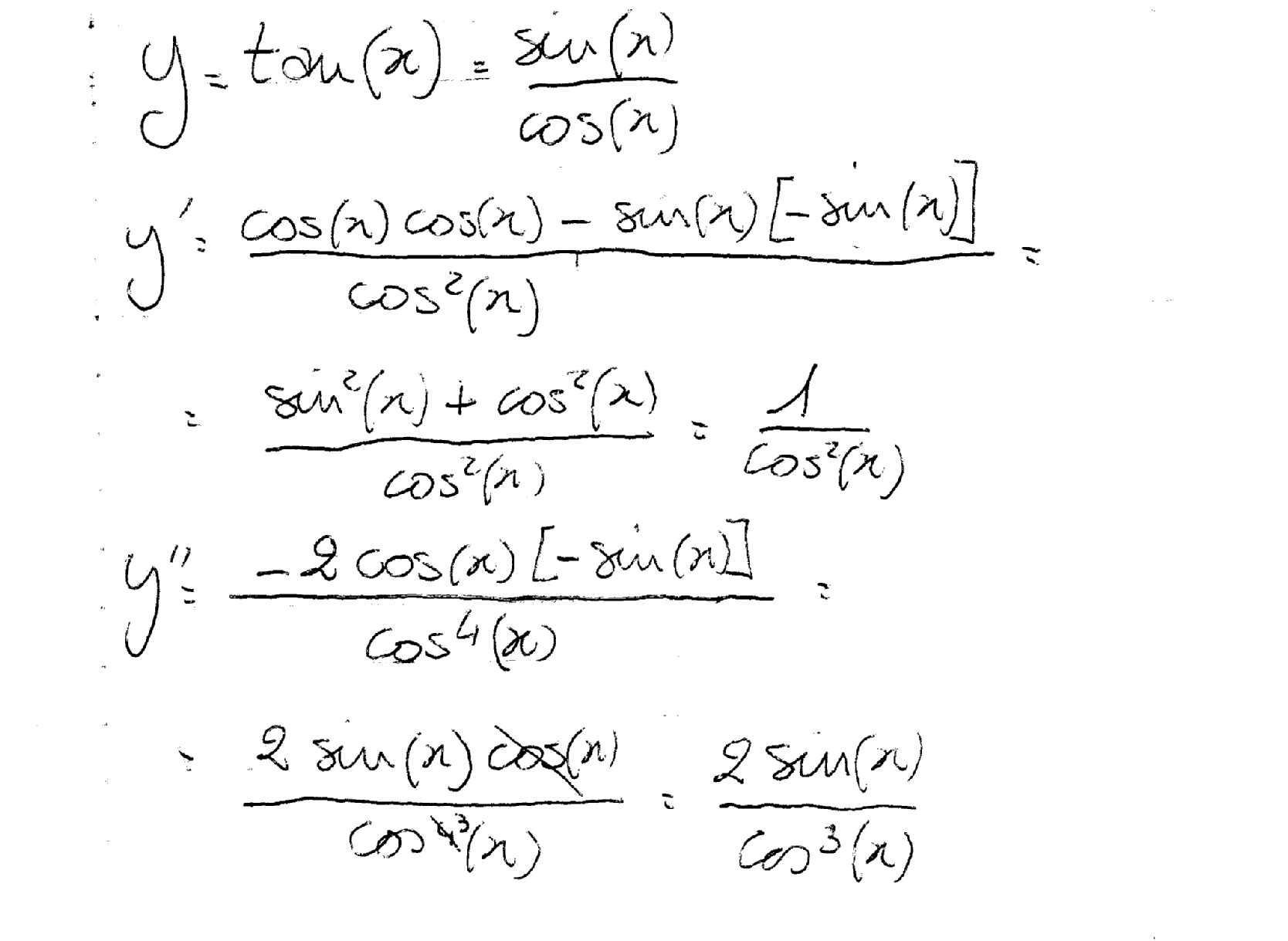



What Is The 2nd Derivative Of Y Tanx Socratic
The derivative for e^(x/y) = x yThis problem is from Single Variable Calculus, by James Stewart,If you enjoy my videos, then you can click here to subscribFind the Derivative d/dy e^ (x/y) ex y e x y Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that d dyf (g(y)) d d y f ( g ( y)) is f '(g(y))g'(y) f ′ ( g ( y)) g ′ ( y) where f (y) = ey f ( y) = e y and g(y) = x y g ( y) = x y Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set u u as x y x y Differentiate the function y = e^(x1) 1




Ex 5 4 1 Differentiate Ex Sinx Chapter 5 Ncert Ex 5 4




7 1 Introductionfunctions And Inverses A Function Is
Y = e x e − x e x − e − x Differentiate using the Quotient Rule which states that d dxf(x) g(x) d d x f ( x) g ( x) is g(x) d dxf(x) f(x) d dxg(x) g(x)2 g ( x) d d x f ( x) − f ( x) d d x g ( x) g ( x) 2 where f(x) = ex e x f ( x) = e x e − x and g(x) = ex e x g ( x) = e x − e − xDifferentiate {eq}\displaystyle y = e^x \bigg(1 \cot \bigg(\dfrac x 2\bigg)\bigg) {/eq} Product Rule In calculus, we calculate the derivative of the product of two functions with the help ofHow to differentiate the natural exponential function using chain rule d/dx of e^(x^2)
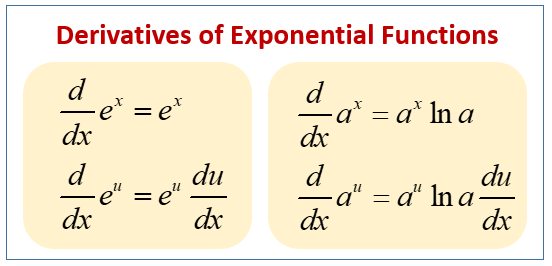



Calculus Exponential Derivatives Examples Solutions Videos




What Is The Derivative Of E X Y 3 X Y Quora
Derivative of e^ {x^3} \square!Implicit Differentiation Proof of e x Let Then Taking the derivative of x and taking the derivative of y with respect to x yields Multiply both sides by y and substitute e x for y Proof of e x by Chain Rule and Derivative of the Natural Log Let and consider From Chain Rule, we get We know from the derivative of natural log, thatSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more



What Is The Derivative Of Y E X 1 E X 1 Quora




Differentiate The Function Y Log 2 E X Cos Pi X Mathematics Stack Exchange
This video looks at how to differentiate the basic exponential function e^x http//wwwmathslearncouk/alevelmathshtmlIt then extends to look at how to diStep 1 Work on the LHS to break up e^ (x y) e^x (e^y) = 3 x y Step 2 Apply implicit differentiation with product rule on the LHS e^x (e^y) (dy/dx) e^x (e^y) = 1 dy/dx Step 3 Transpose dy/dx from RHS to LHS and e^x (e^y) from LHS to RHS e^x (e^y) (dy/dx) dy/dx = 1The Derivative Calculator supports computing first, second, , fifth derivatives as well as differentiating functions with many variables (partial derivatives), implicit differentiation and calculating roots/zeros You can also check your answers!
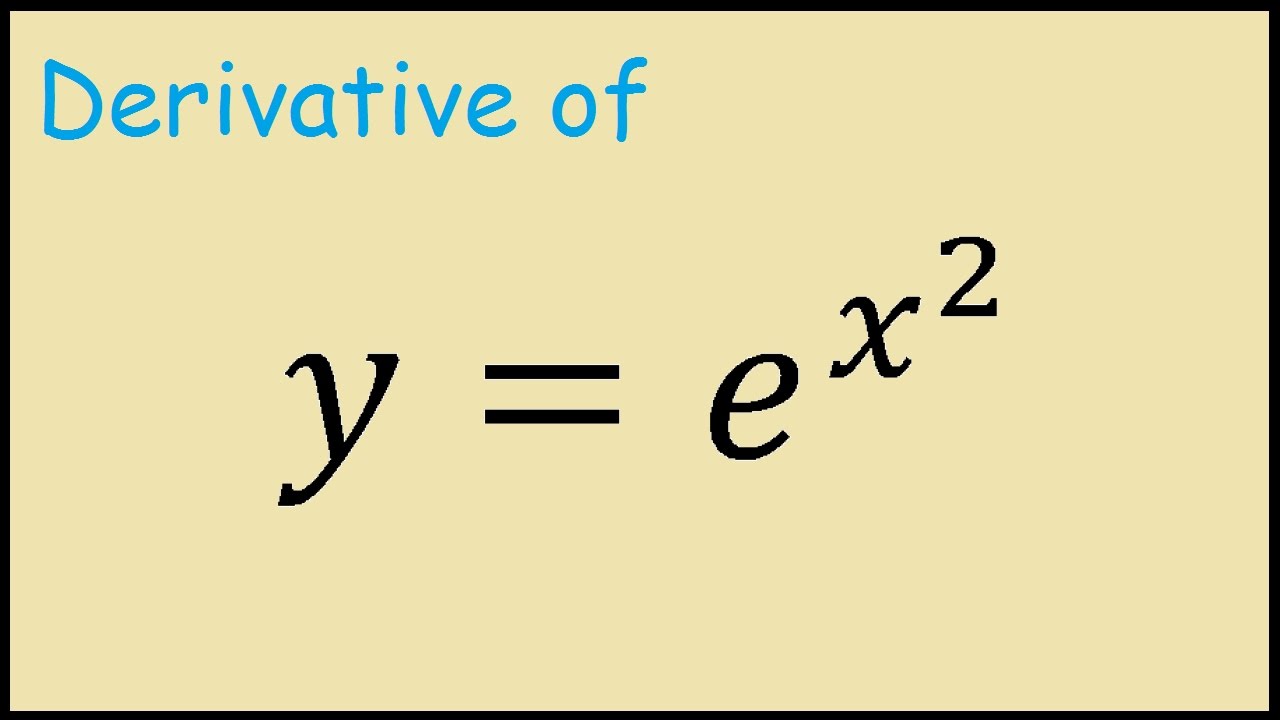



Derivative Of Y E X 2 Youtube




Derivative Rules
Answer and Explanation 1 Given differential equation xdy dx y = ex, x > 0 x d y d x y = e x, x > 0 Multiplying both sides by dx d x , we get x dy y dx = ex dx x d y y d x = e x d x The notation f (x,y)= e xy implies that x and y are independent variables Without further information, you can find or but not dy/dx If, for example, you know that f (x,y)= e xy = constant, then you can use "implicit differentiation" (1 dy/dx)e xy = 0 and determine that dy/dx= 1 Share ShareThis calculus video explains how to find the derivative of x^x^x using a technique called logarithmic differentiation which is useful for differentiating exp




Ex 5 4 2 Differentiate E Sin 1 X Teachoo Ex 5 4




Exponential Function Wikipedia
Xy=e^x/e^y => y*e^y = x^(1)*e^x differentiating wrt x => y'*e^yy*e^y*y' = (1)e^x/x^2 x^(1)*e^x => (1y)*e^y*y' = x^(1)*e^xe^x/e^2 => y' = {x^(1)*e^xe use chain rule, ie, you have to first differentiate first e^(some value) multiplied by the differentiation of the value which is there in exponential so, differentiation of e^(some value) = e^(some value) therefore, dy/dx = {e^(axb)}*a here, the last term a comes from the differentiation of axbI think i am differentiating with respect to x Homework Equations Derivative of y^x is y^x The Attempt at a Solution I don't know if I should use the chain rule or treat it like y^x When i used the chain rule I got ye^y1, but then I




Ex 5 5 15 Find Dy Dx Of Xy E X Y Class 12 Ex 5 5




What Is The Derivative Of E X Wrt Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



Derivative Calculator With Steps



Chain Rule In Differentiation Of E X From First Principles The Student Room




Differentiate The Function Y Ex 7 5 6x 5 Chegg Com
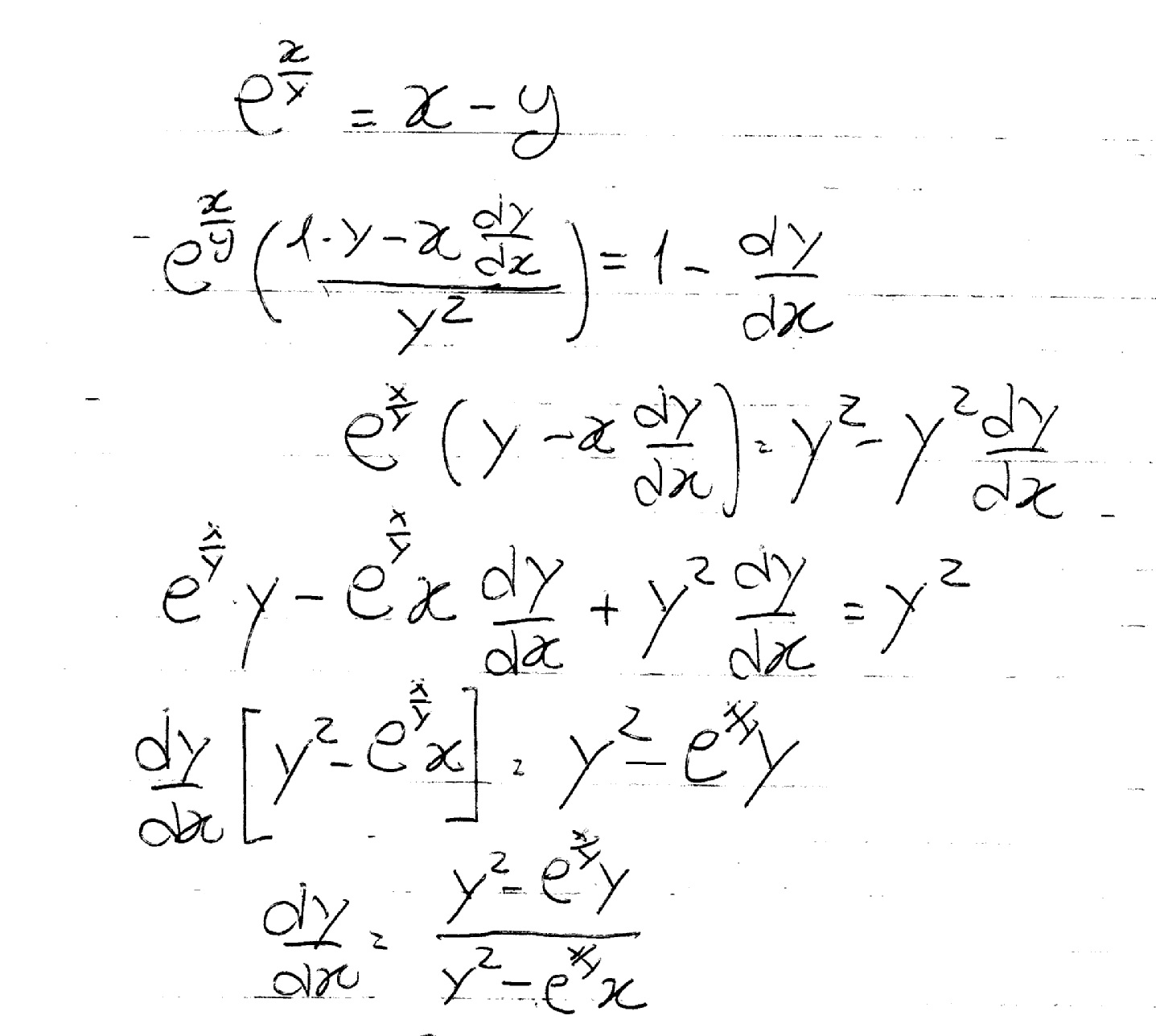



How Do You Implicitly Differentiate E X Y X Y Socratic
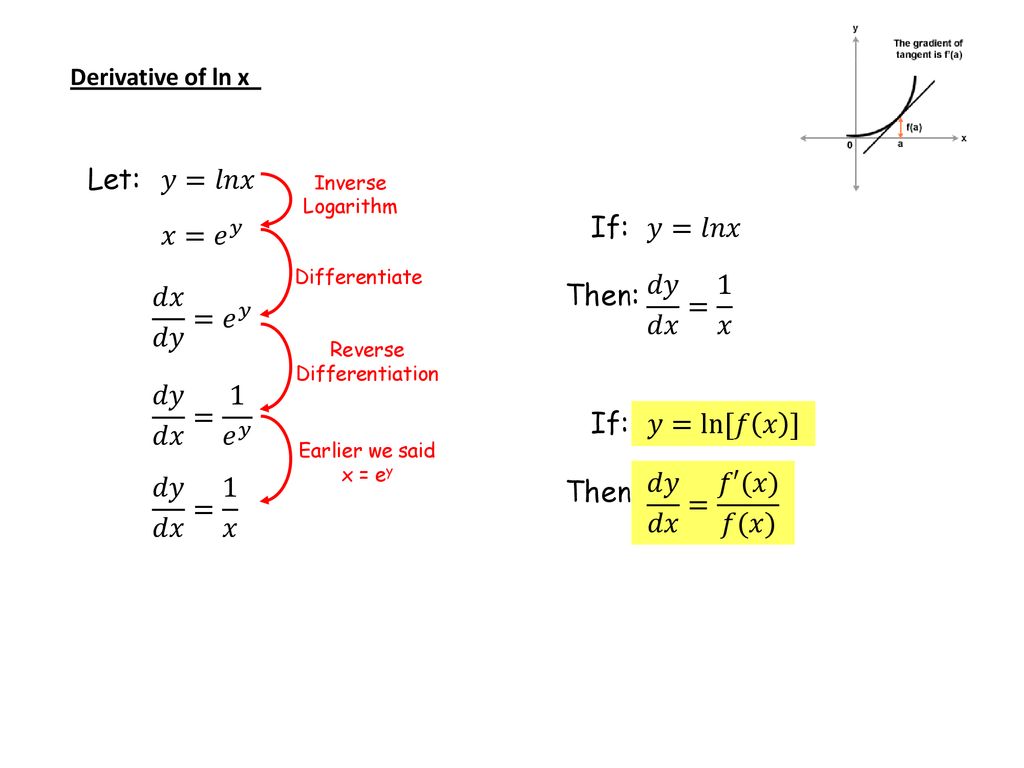



Derivatives Ex Ln X Ppt Download
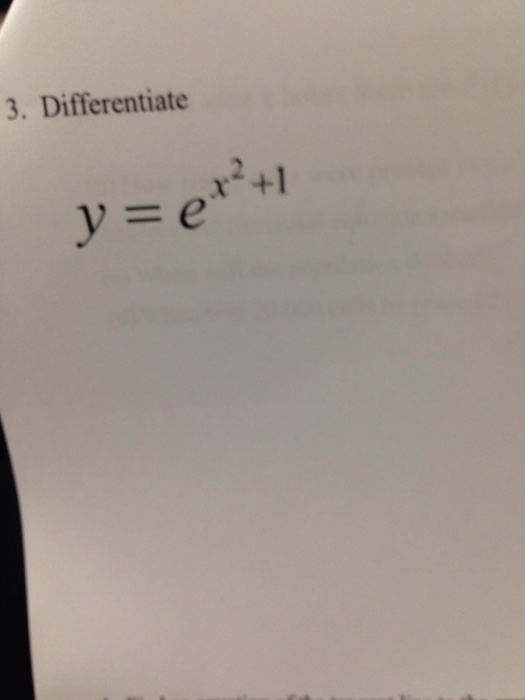



3 Differentiate Y E X 2 1 Chegg Com




Differentiate With Respect To X I Y Xlnx Ii Y X




Find The Derivative Of E X Sin X With Respect To X




Differentiate X 1 X 3 Novocom Top



How Do You Use The Chain Rule To Differentiate Y Cos Sqrt 8t 11 Socratic
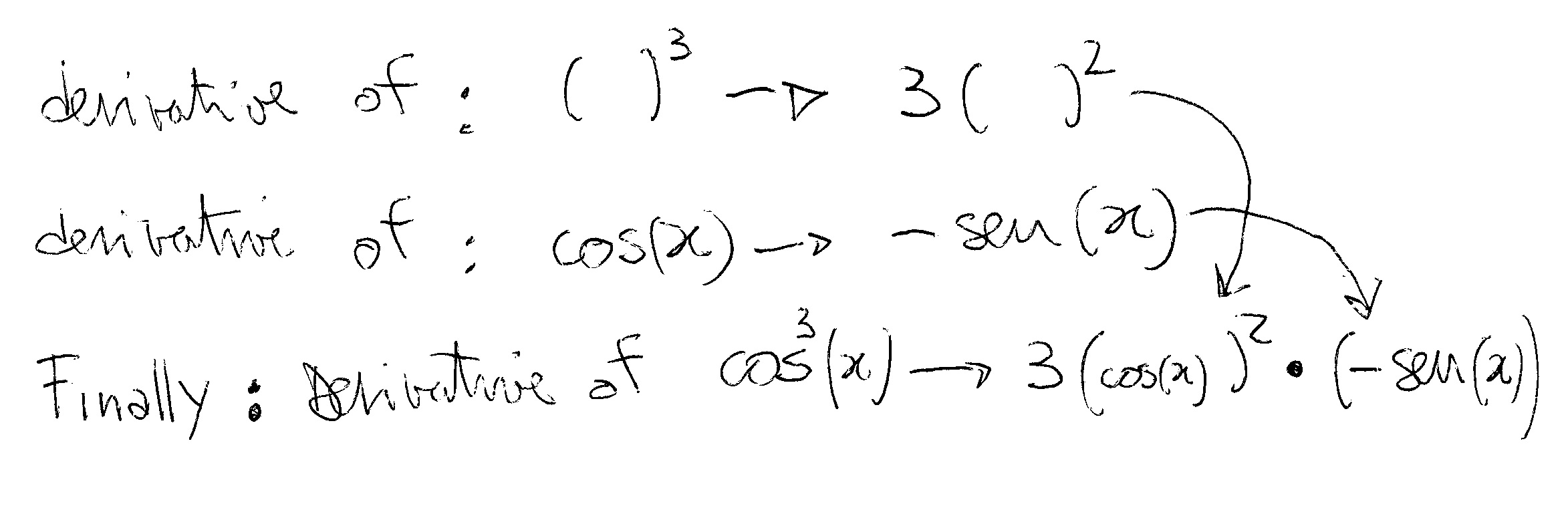



What Is The Derivative Of Cos 3 X Socratic




Derivatives Of Inverse Functions Video Khan Academy




Chapter 3 3 Practice Problems




Solved Differentiate Y E 2 X With Respect To X Self Study 365



1



If X Y E X Y What Is Dy Dx Quora



1




Answered Differentiate The Function Y Ex 6 Bartleby




Derivatives Ex Ln X Ppt Download




How Do You Differentiate E Xy Use Implicit Differentiation Youtube




8 10 Pointsscalcet8 3 1 032 Differentiate The Chegg Com
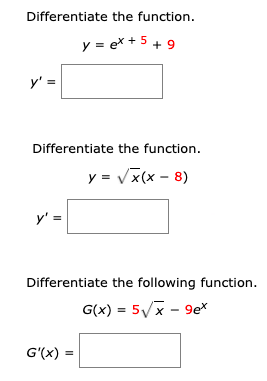



Differentiate The Function Y Ex 5 9 Y Chegg Com




How To Find Derivatives Of Implicit Functions Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
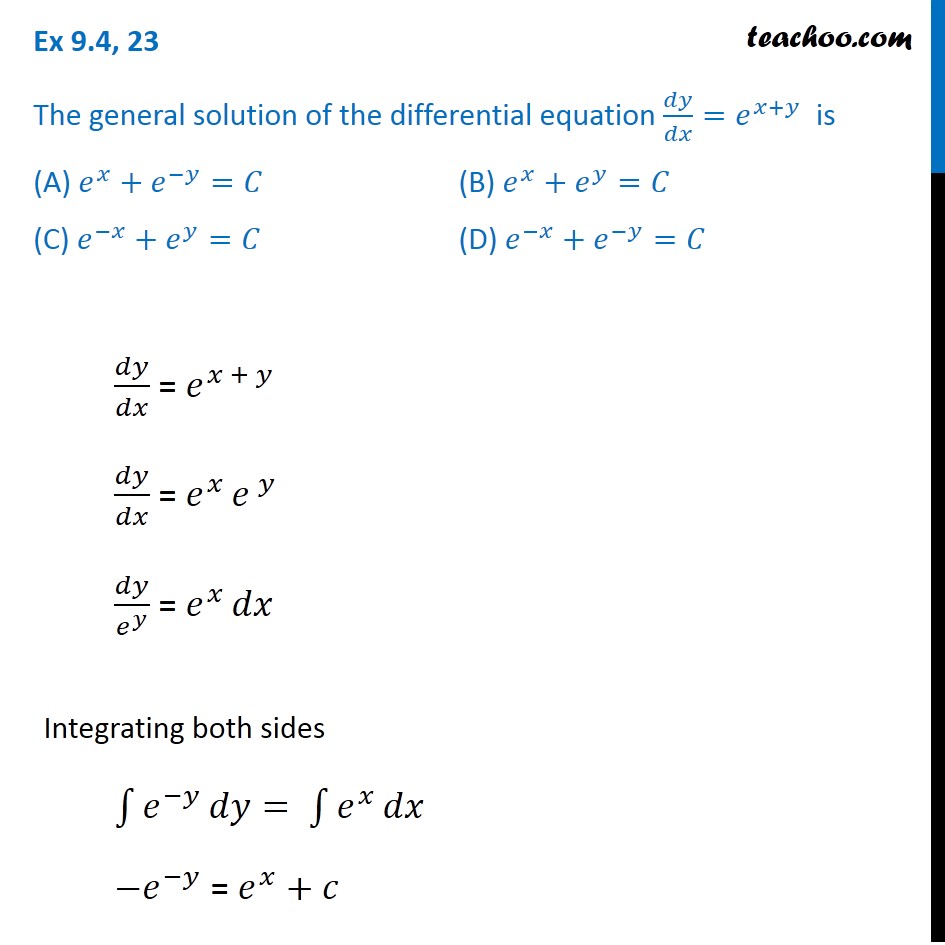



Ex 9 4 23 General Solution Of Dy Dx E X Y Is A E X E Y C



If X Y E X Y Show That Dy Dx Logx Log Xe 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
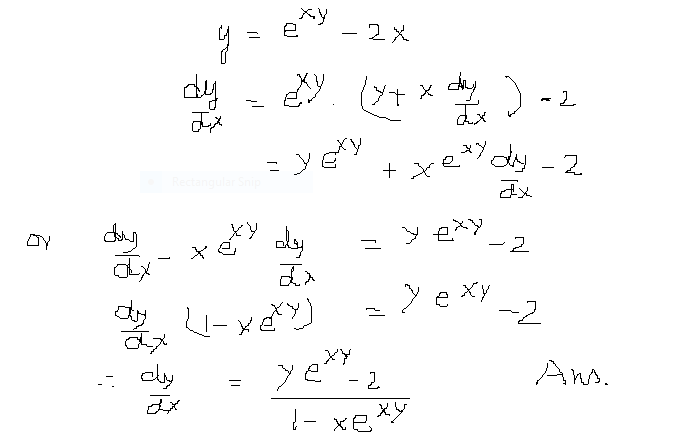



How Do You Differentiate Y E Xy 2x Socratic




Solution Differentiate Y E X Cos X 2
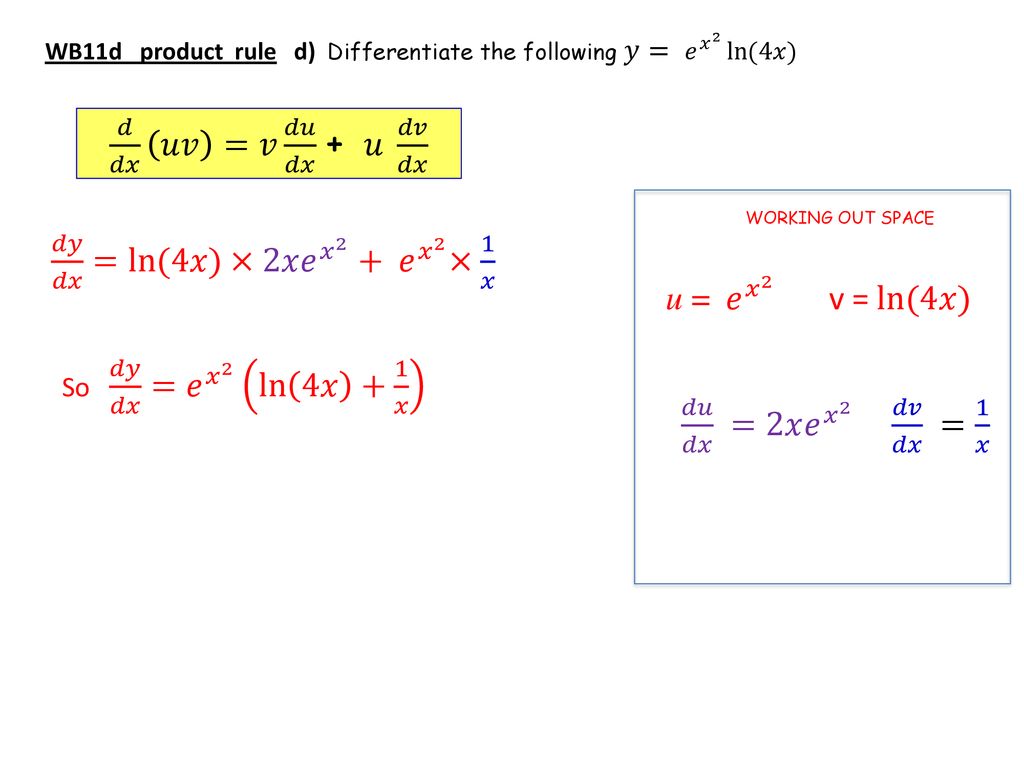



Derivatives Ex Ln X Ppt Download



Differentiate Y E X 7x 2 Y Chegg Com



How To Differentiate Y E Tanx Quora
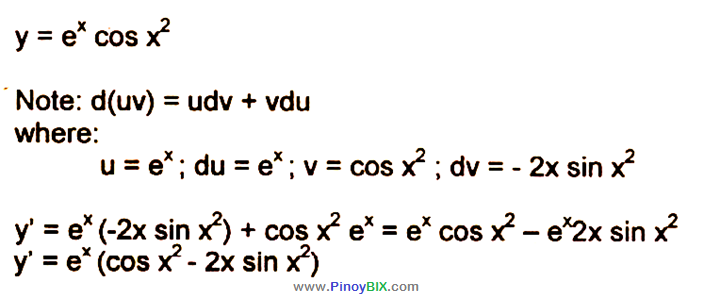



Solution Differentiate Y E X Cos X 2
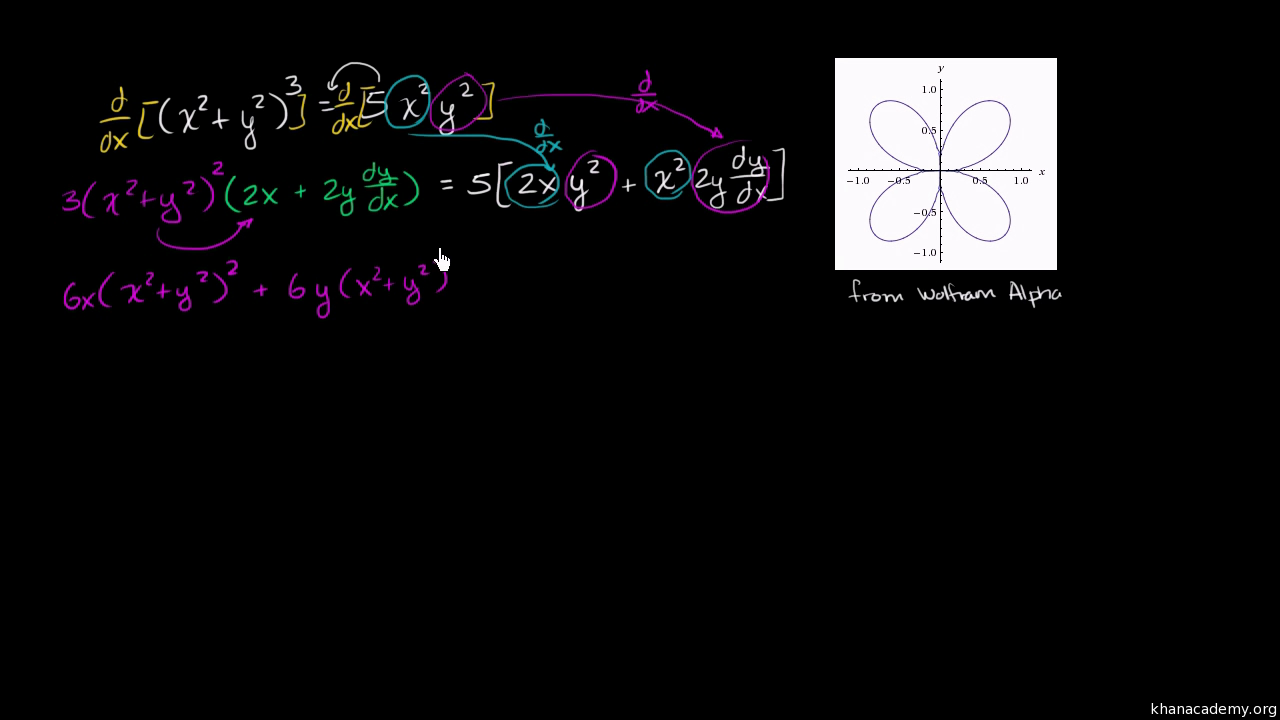



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy



Differentiate Y E Cos X Youtube
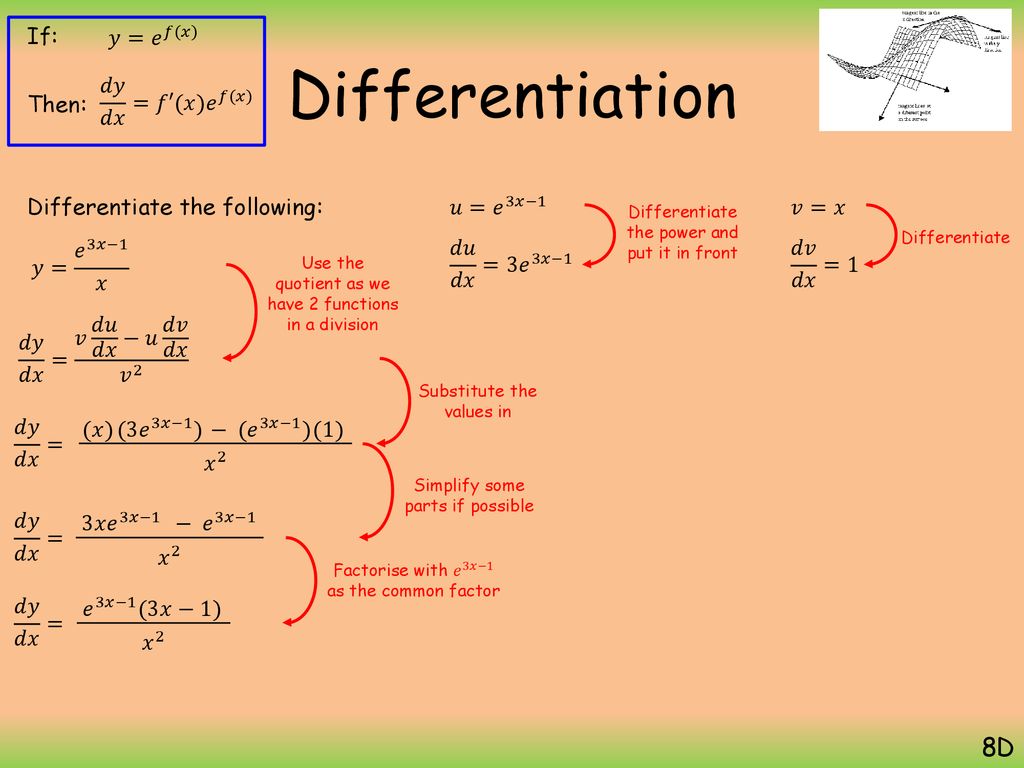



Differentiation Ppt Download



How To Differentiate Ln E 2x E X 1 Derivative Differentiation Collection Chain Rule Cr9 Ap Calc Youtube



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




Answered 5 Differentiate The Following A Y Bartleby
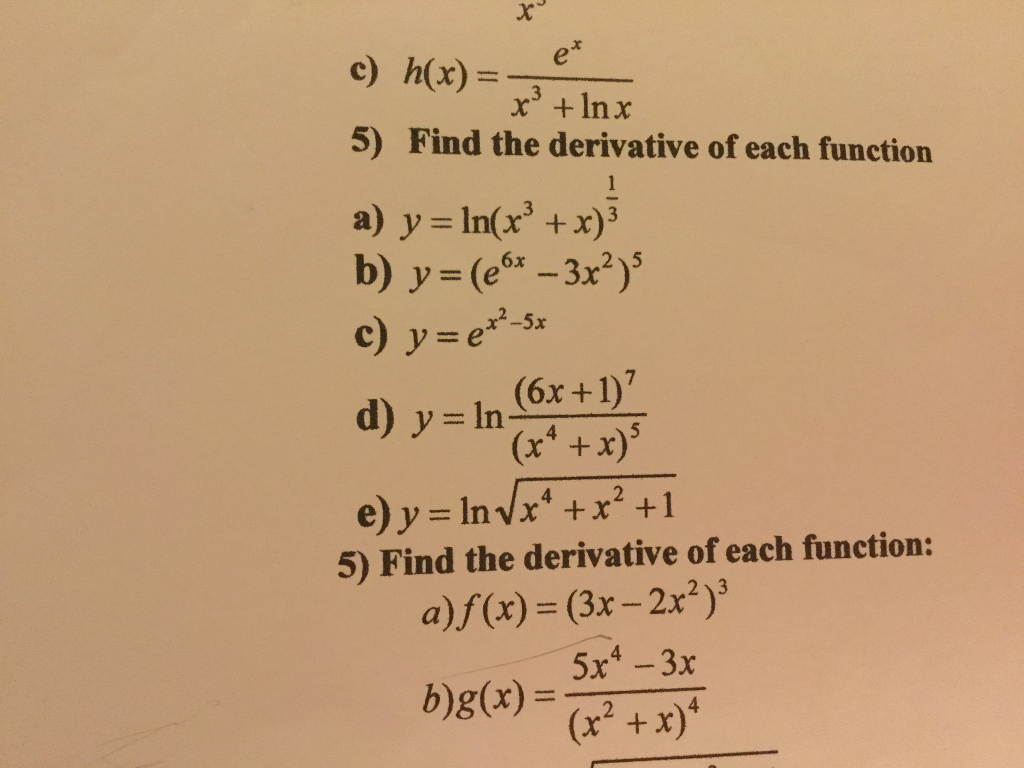



Find The Derivative Of Each Function Y Ln X 3 Chegg Com
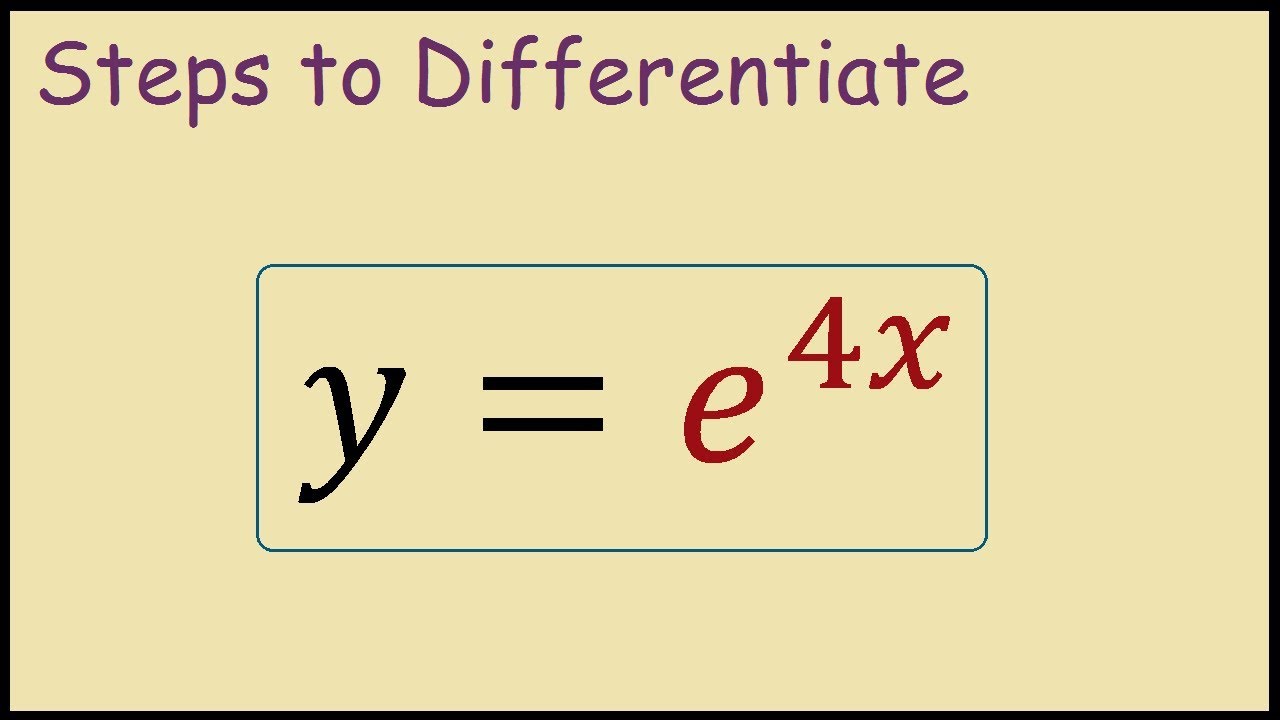



How To Differentiate E 4x Chain Rule Youtube
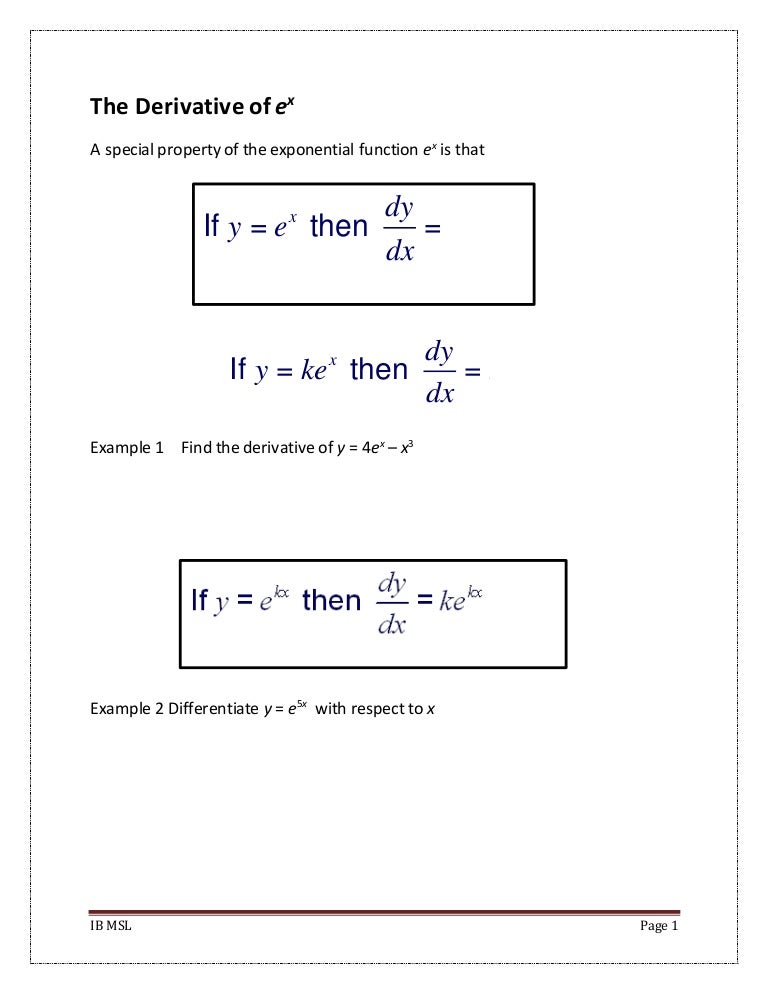



The Derivative Of E X And Lnx
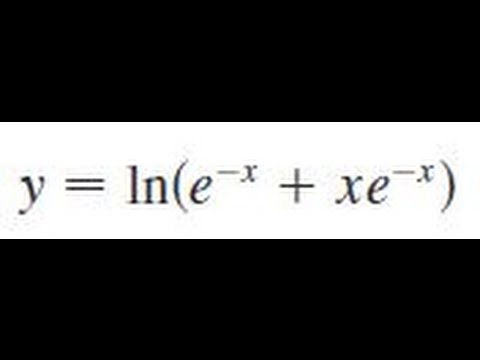



Y Ln E X Xe X Differentiate The Function Youtube




Differentiate X 1 X 3 Novocom Top




Differentiation Of The Exponential Function E X And Natural Logarithms Lnx Exponential Function E X Ppt Download
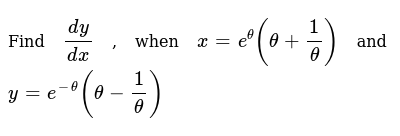



Find Dy Dx When X E Theta Theta 1 Theta And Y E Th




Derivative Of E Y 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Derivative Of E X Using The Inverse Function Method Youtube




If Y Sqrt 1 E X 1 E X S Howt H A T Dy Dx E X 1 E X Sqrt 1 E 2x Youtube



Q Tbn And9gcrlw5wx6qxsllz2r9p3fgzffnje5hqap6knkskthxk8e15jx7e4 Usqp Cau
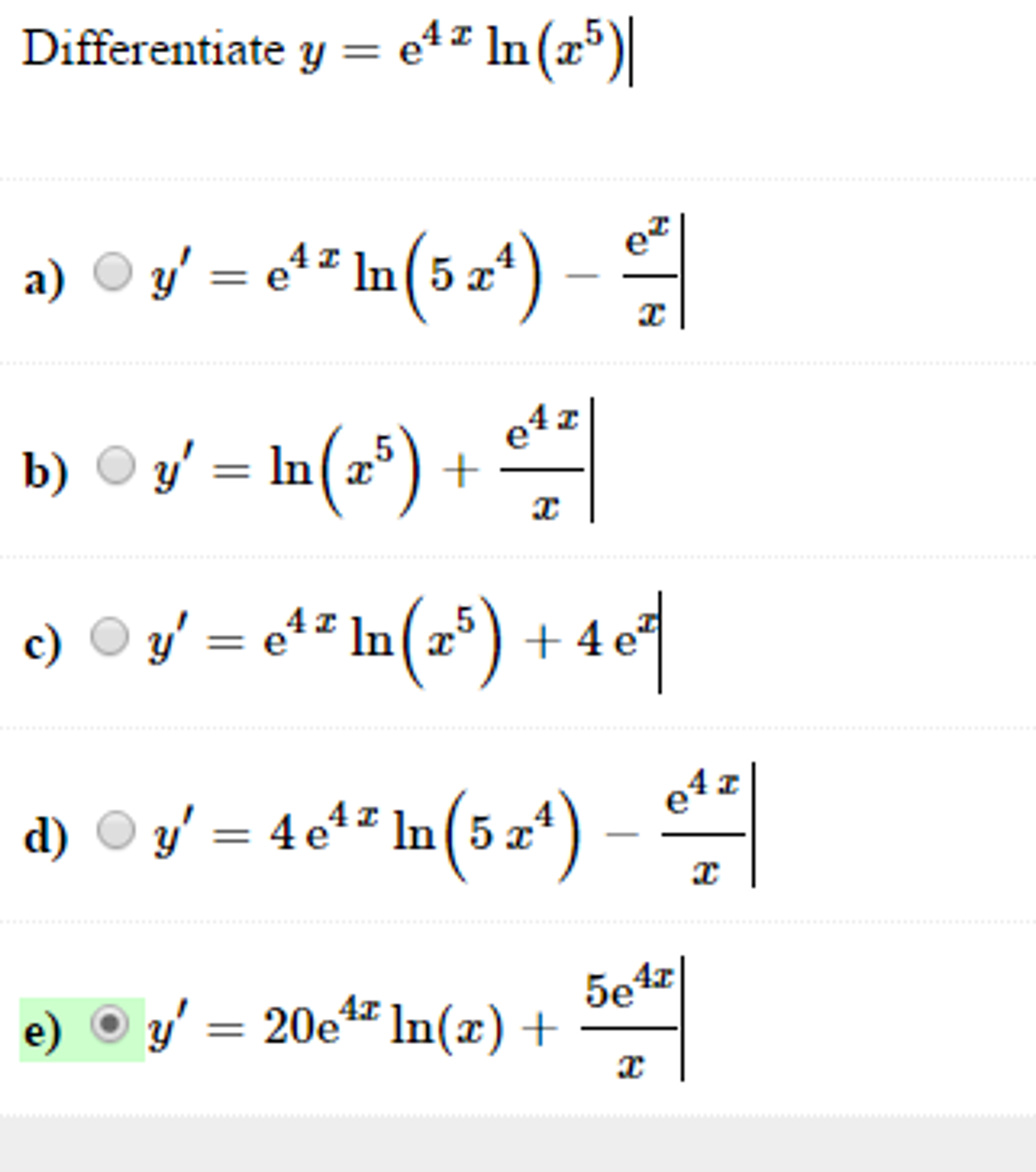



Differentiate Y E 4x Ln X 5 Y E 4x In 5 X 4 Chegg Com



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




How To Differentiate Negative Exponentials




Answered Differentiate Y E Cos X U 3 Bartleby




Ex 5 4 6 Ex 5 4




Find Dy Dx Of Function Xy E X Y Mathematics Shaalaa Com



6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function




Derivatives Of Exponential Logarithmic Functions Ppt Download
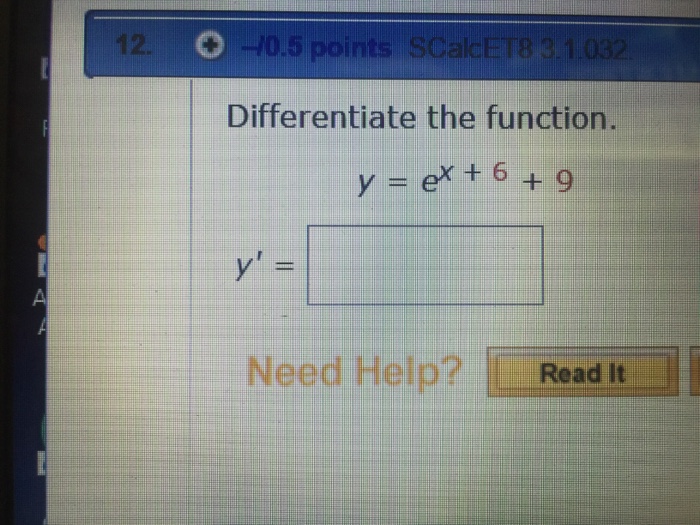



Differentiate The Function Y E X 6 9 Chegg Com




Differentiate With Respect To X Y E Ax E Ax Study Com




Ex 5 4 10 Differentiate W R T X In Cos Log X E X Teachoo



What S The Derivative Of Math Y E X E X E X Cdots Math Quora




Chain Rule Wikipedia
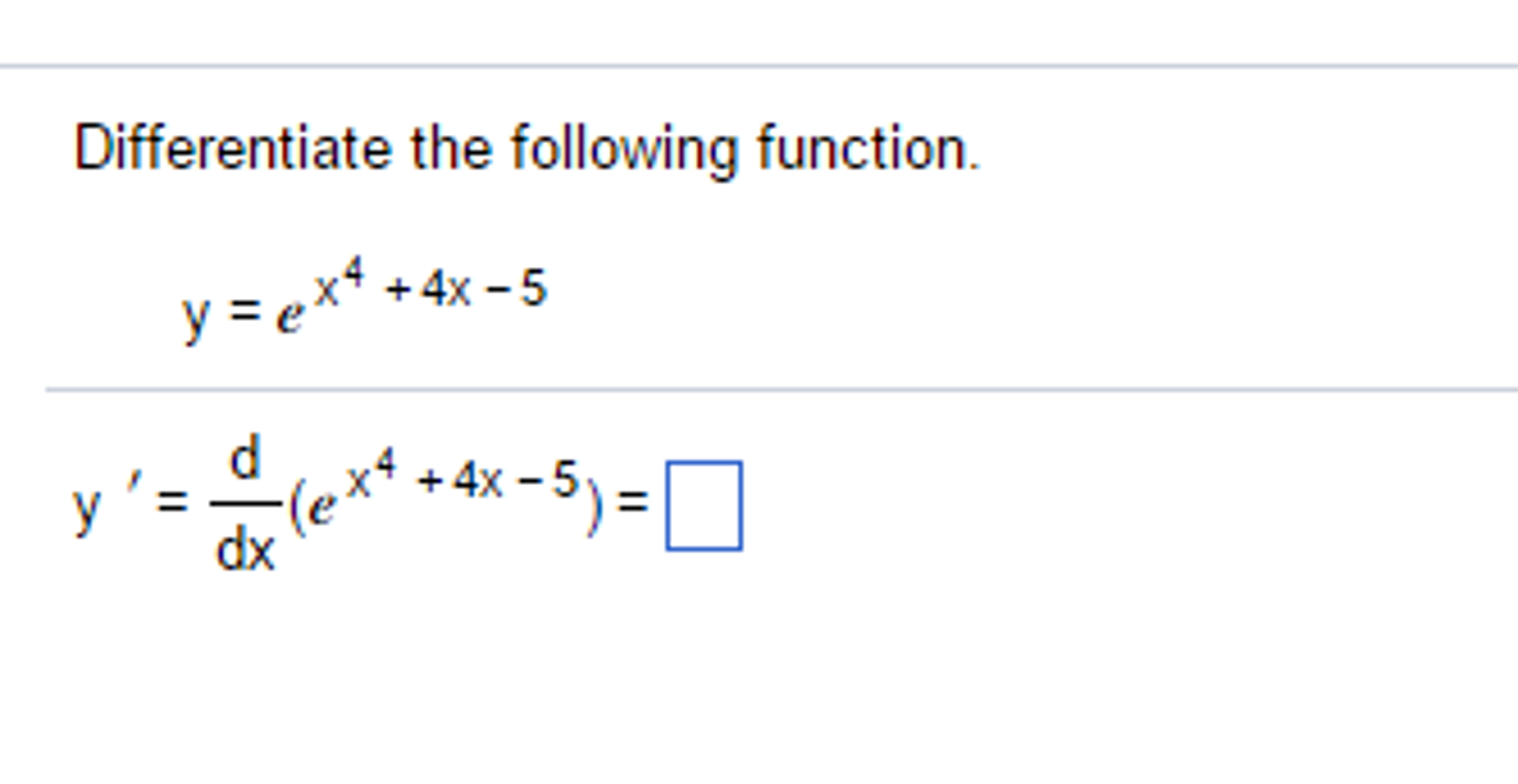



Differentiate The Following Function Y E X 4 4x Chegg Com
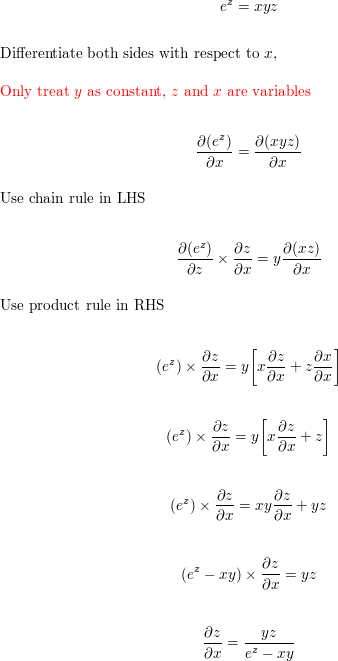



Use Implicit Differentiation To Find Z X And Z Y Ez Xyz Homework Help And Answers Slader
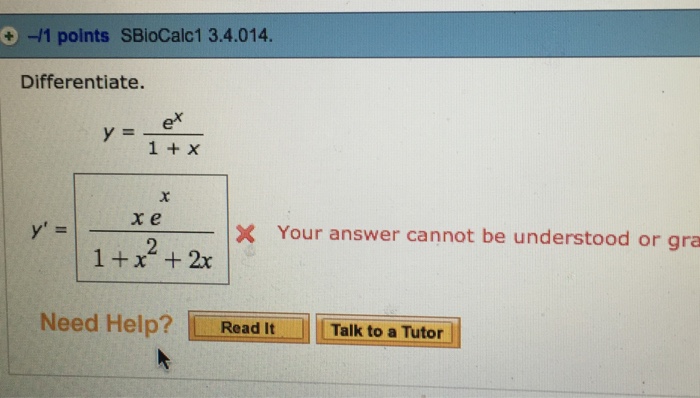



Differentiate Y E X 1 X Y Xe X 1 X 2 2x Chegg Com
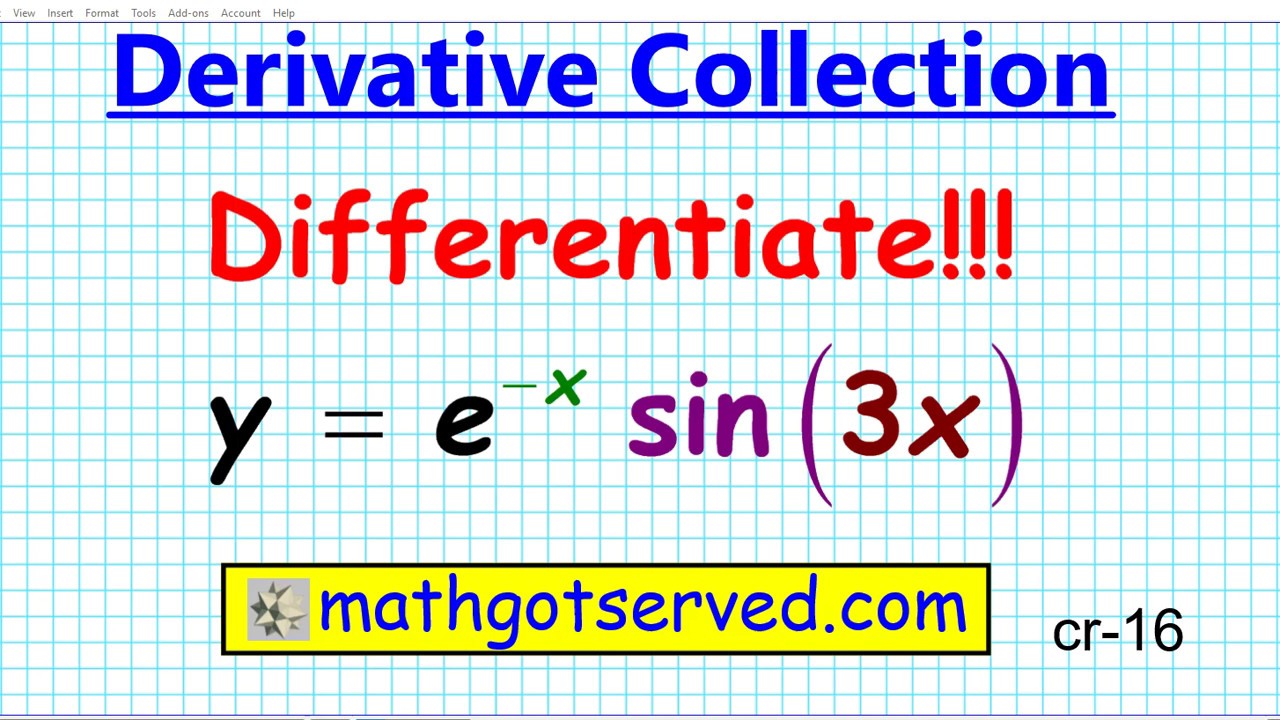



How To Find The Differentiate E X Sin 3x Chain Rule Derivative Collection Ap Calc Calculus Cr 16 Youtube
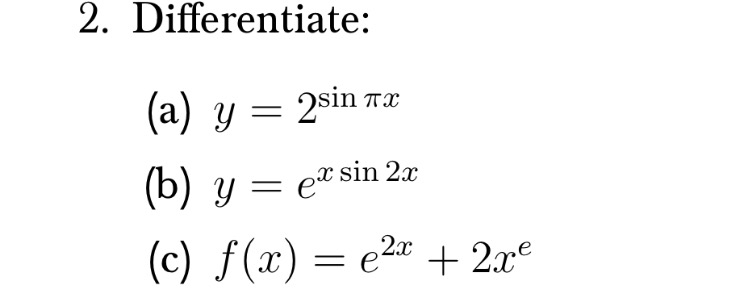



Differentiate A Y 2 Sin Pix B Y E X Sin 2x Chegg Com
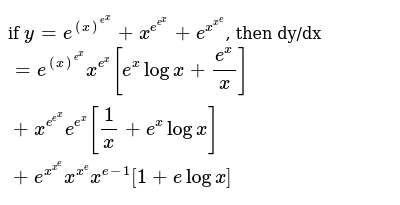



If Y E X E X X E E X E X X E Then Dy
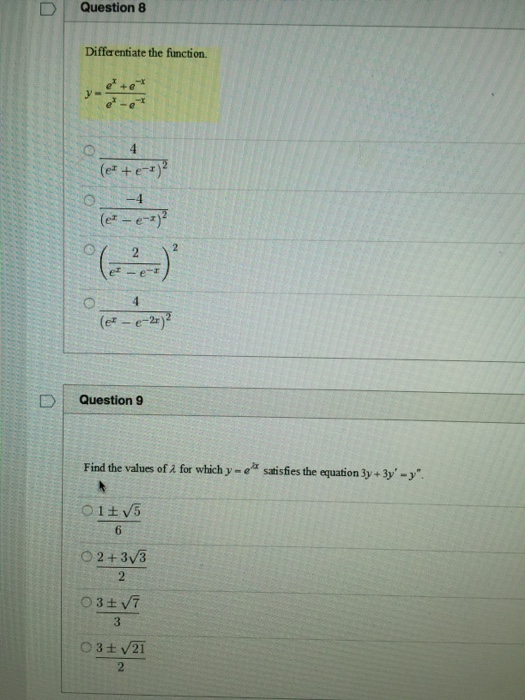



Differentiate The Function Y E X E X E X E X Chegg Com
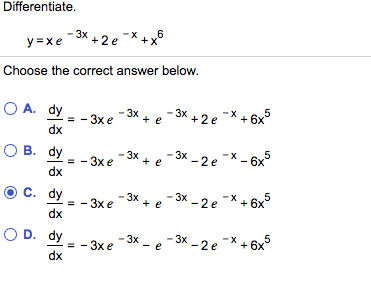



Differentiate Y X E 3x 2 E X X 6 Choose Chegg Com



How To Differentiate Y E Xlogx X 2 Quora




Ex 9 3 5 Form Differential Equation Y Ex A Cos X B Sin X
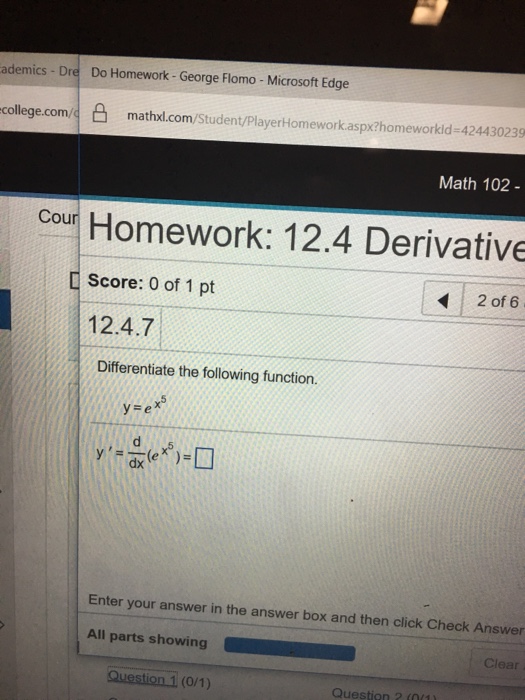



Differentiate The Following Function Y E X 5 Y Chegg Com




Find Dy Dx When Y E Xlog 1 X 2




How Do You Implicitly Differentiate 2 E Xy 2 Xy Y 2x 3 Y Socratic
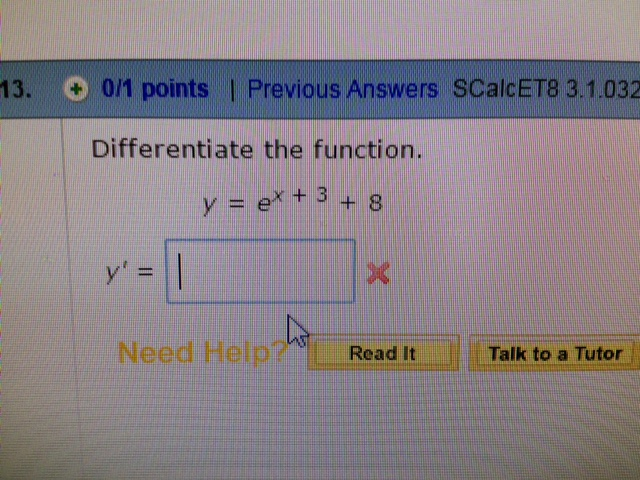



Differentiate The Function Y E X 3 8 Chegg Com



Q Tbn And9gcq9arl5ab K Kkztqdma6czzlslnfprp6ljv7o6a18 5qqda4yy Usqp Cau




Derivative Of 𝑒ˣ Video Khan Academy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿